No products in the cart.
ELISA Sensitivity and Specificity Problems
Coating as a Sensitivity factor in ELISA
ELISA Sensitivity and Specificity Problems is related to quality of ELISA Coating,ELISA Blocking, HRP-Conjugate quality and Cross-reaction.In the indirect ELISA tests, quality of coated Ag is the most important factor for ELISA test sensitivity. Target protein should be part of whole Ag that immune system can well recognize it and produce different Ab classes and sub-classes against. In fact, for sensitive ELISA test, we need High affinity Abs that usually is produces against surface Ags which are mostly are produces against surface soluble proteins. Also, during Ag extraction make sure that 3rd Structure of protein keep safe.
In Sandwich and competitive ELISA tests, monoclonal Ab affinity is the most important factor. In Sandwich ELISA make sure that the target epitopes in coating and conjugate are not same or even close together because it can reduce total Ag-Ab-Ag complexes during incubation and reduce the sensitivity of all tests.
HRP-Conjugate stabilizers & other reaction buffers as Sensitivity factor in ELISA tests
Another important factor in sensitivity of ELISA tests is quality of the HRP-Conjugate stabilizers other ELISA reaction buffers. Recovery of ELISA Conjugate buffer and sample diluent should be almost the same as human serum. Also, even high concentration of NaCl in buffer can reduce nonspecific binding reduce the overall background but at the same time it can reduce ELISA tests sensitivity significantly.
Detergent’s structure and concentration is important too, some detergents such as Nonidet-P40, SDS, Tween-80 and Triton-X100 are not compatible with ELISA tests. Tween-20 is the best choice, but it can make aggregation in proteins in long-term storage.
ELISA Sensitivity and Specificity Problems
ELISA Blocking solution and low ELISA test sensitivity
ELISA Blocking Buffers usually contain BSA, Casein and a little amount of PVP, PEG, Gelatin, and other polymers. High concentration of PVP, PEG, Gelatin usually make difficulties in ELISA test sensitivity. This small amount of PVP, PEG, Gelatin should be dissolved in ELISA reaction buffer to allow Abs to react with Ags. Low temperature worsens the situation and tests usually need more time to be complete. So, it is important to bring all reaction buffers and plate temperature to RT before starting ELISA tests.
How Coating affects ELISA specificity?
ELISA coating can drastically impact ELISA tests Specificity. In direct and indirect ELISA tests purity of Coated Ag is crucial factor for test specificity. Usually, 99 and more purity is suitable for direct and indirect ELISA coating. Also, the host of synthetic proteins is important, E coli host usually have more cross reactivity and less specificity from yeast hosts. But the method of extraction of protein is as important as the host. Chromatography separation, precipitation methods and general lysing usually lead to poor results compared to Immunochromatography and secreted Ag separation. Any impurity can result in cross reaction and made ELISA tests to be less specific. You need to use 1 to 3.5 ng/ml of your Ag in coating buffer. The more concentration, the less specificity will achieve in ELISA tests.
Cross-reaction can affect Direct and indirect ELISA test specificity
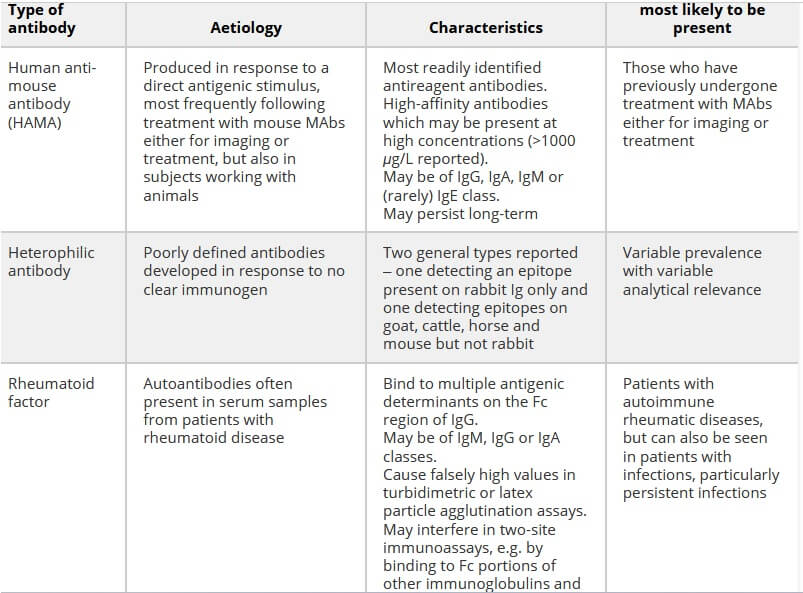
Well-designed ELISA kits specificity is more than 95%. Sometimes it can be less (more than 85%). For example, in campylobacter ELISA kits have a range of specificity from 83-90%, because it has extensive cross reaction with other bacteria. Human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA), rheumatoid factor (RF), and heterophile antibodies are responsible for causing false-positive immunoassay results. HAMA, RF and heterophile antibodies should be blocked by ELISA HAMA Blocker diluent to eliminate the most strong false positive results in ELISA tests.
Normally RF and heterophile antibodies is block by ELISA sample diluents. In some cases, high bilirubinemia, lipemia and hemolysis can result in false positive results. Remember that false positive ELISA results make poor ELISA specificity test results while False negative affects ELISA tests sensitivity results. Most false negative results depend on ELISA buffers poor recovery, Hook effect and low affinity Abs.
Cross-reaction can affect Sandwich ELISA test specificity
Well-designed ELISA kits specificity is more than 95%. Sometimes it can be less (more than 85%). For example, in campylobacter ELISA kits have a range of specificity from 83-90%, because it has extensive cross reaction with other bacteria. Human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA), rheumatoid factor (RF), and Heterophile antibodies are responsible for causing false-positive immunoassay results. HAMA, RF and heterophile antibodies should be blocked by ELISA HAMA Blocker diluent to eliminate the most strong false positive results in ELISA tests.
Normally RF and heterophile antibodies is block by ELISA sample diluents. In some cases, high bilirubinemia, lipemia and hemolysis can result in false positive results. Remember that false positive ELISA results make poor ELISA specificity test results while False negative affects ELISA tests sensitivity results. Most false negative results depend on ELISA buffers poor recovery, Hook effect and low affinity Abs.
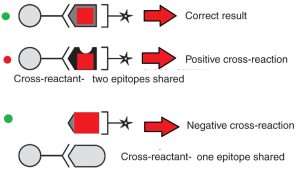
ELISA Cross reactions
Some different Ags have similar epitopes. For example, HCG, LH, FSH and TSH are very close epitopes that can cause in sever cross reactions. Most poly clonal abs against these Ag have more than 30% cross reactivity that can result in false positive signals in these tests. Using Anti beta- chain monoclonal Abs can solve the problem but remember that even monoclonal antibodies can show sever cross reaction in these Ags, especially when it comes to Alfa-Chain of BHCG and LH. For determining this type of cross-reaction, you need to run for instance LH test in BHCG kit and so on!
HAMA, RF and heterophile antibodies is important in Sandwich ELISA too, so it should be blocked by ELISA HAMA Blocker diluent to eliminate the most strong false positive results. Normally RF and heterophile antibodies is block by ELISA sample diluents. In some cases, high bilirubinemia, lipemia and hemolysis can result in false positive results.